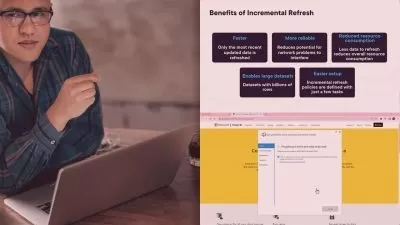
Data Analyst-Python/ETL/SSIS/SSRS/SSAS/Microsoft SQL/PowerBI
Tech Academy
10:59:23
Description
Learn Data Analyst Skills : Connect | Clean | Transform | Model | Interpret | Analyse |and Visualise data
What You'll Learn?
- Analyse Data with Python
- Visualise Data with Python
- Clean Data with Python
- Create an ETL Process
- Create SSIS Package to Extract, Transform and Load Data
- Create reports with SSRS
- Create a Tabular Model with SSAS
- Create Key Performance Indicators - KPI's
- Create calculated columns
- Creating measures
- Analyse data with SSAS
- Analyse data with Microsoft SQL (T-SQL)
- Connect to multiple data sources with Power BI
- Analyse data with Power BI
- Visualise data with Power BI
- Analyse and visualise data on SQL Server Database with Power BI
Who is this for?
More details
DescriptionData is everywhere. Everything you do online and in your daily life generates data—and it’s a valuable business resource. In fact, 94% of companies say data and analytics are essential to their growth. As we move toward greater digitization, there is an ever-increasing demand for professionals who can turn information into actionable insights.
A data analyst is a person whose job is to gather and interpret data in order to solve a specific problem. The role includes plenty of time spent with data but entails communicating findings too.
Here’s what many data analysts do on a day-to-day basis:
Gather data: Analysts often collect data themselves. This could include conducting surveys, tracking visitor characteristics on a company website, or buying datasets from data collection specialists.
Clean data: Raw data might contain duplicates, errors, or outliers. Cleaning the data means maintaining the quality of data in a spreadsheet or through a programming language so that your interpretations won’t be wrong or skewed.
Model data: This entails creating and designing the structures of a database. You might choose what types of data to store and collect, establish how data categories are related to each other, and work through how the data actually appears.
Interpret data: Interpreting data will involve finding patterns or trends in data that could answer the question at hand.
Present: Communicating the results of your findings will be a key part of your job. You do this by putting together visualizations like charts and graphs, writing reports, and presenting information to interested parties
During the process of data analysis, analysts often use a wide variety of tools to make their work more accurate and efficient. Some of the most common tools in the data analytics industry include:
Microsoft Excel
Google Sheets
SQL
Tableau
R or Python
SSAS
SSRS
SSIS
ETL
Microsoft Power BI
Jupyter Notebooks
Who this course is for:
- Beginner Data Analyst
- Beginner Data Scientist
- Beginner Business Intelligence Analyst
Data is everywhere. Everything you do online and in your daily life generates data—and it’s a valuable business resource. In fact, 94% of companies say data and analytics are essential to their growth. As we move toward greater digitization, there is an ever-increasing demand for professionals who can turn information into actionable insights.
A data analyst is a person whose job is to gather and interpret data in order to solve a specific problem. The role includes plenty of time spent with data but entails communicating findings too.
Here’s what many data analysts do on a day-to-day basis:
Gather data: Analysts often collect data themselves. This could include conducting surveys, tracking visitor characteristics on a company website, or buying datasets from data collection specialists.
Clean data: Raw data might contain duplicates, errors, or outliers. Cleaning the data means maintaining the quality of data in a spreadsheet or through a programming language so that your interpretations won’t be wrong or skewed.
Model data: This entails creating and designing the structures of a database. You might choose what types of data to store and collect, establish how data categories are related to each other, and work through how the data actually appears.
Interpret data: Interpreting data will involve finding patterns or trends in data that could answer the question at hand.
Present: Communicating the results of your findings will be a key part of your job. You do this by putting together visualizations like charts and graphs, writing reports, and presenting information to interested parties
During the process of data analysis, analysts often use a wide variety of tools to make their work more accurate and efficient. Some of the most common tools in the data analytics industry include:
Microsoft Excel
Google Sheets
SQL
Tableau
R or Python
SSAS
SSRS
SSIS
ETL
Microsoft Power BI
Jupyter Notebooks
Who this course is for:
- Beginner Data Analyst
- Beginner Data Scientist
- Beginner Business Intelligence Analyst
User Reviews
Rating
Tech Academy
Instructor's Courses
Udemy
View courses Udemy- language english
- Training sessions 121
- duration 10:59:23
- Release Date 2023/02/12
















![SQL Mastery: Learn Enough SQL To Be A Professional [2023]](https://traininghub.ir/image/course_pic/15324-x225.webp)