Unlock P&ID Preparation Guidelines and Common Practices
Boostrand Training,Boostrand PE
5:02:28
Description
Discover the details, operation, maintenance, and safety guidelines of piping and instrumentation diagrams
What You'll Learn?
- Workflow of P&ID issuance and its role in a project
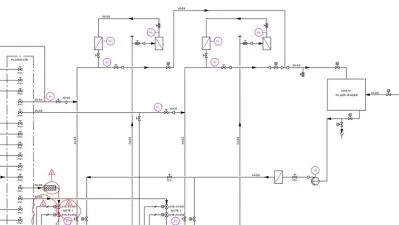
- Details shown on a P&ID for piping, fittings, instruments, scope definition, ...etc.
- Anatomy of the P&ID and P&ID types
- P&ID Guidelines to ensure easy Plant Operation, startup and performance indication
- Isolation of equipment for maintenance
- Plant Drainage System
- Maintenance and Steam Out Requirements
- Plant Depressurization and Blowdown
- P&ID guidelines for Process Safety
- Expected Plant Hazards and Upset Conditions
- Warn the Operator to respond against upsets through Alarms
- Prevent Hazard by Process / System Shutdown
- Mitigate Hazard using Process Safety Valves
- Proper Equipment Design Conditions to Ensure Inherently Safe Operation
- Control and Shutdown Valve Fail Safe Positions
- HAZOP and SIL Assessment of a P&ID
Who is this for?
What You Need to Know?
More details
DescriptionWhat is this Course About?
Explore the details and structure of P&IDs, and gain practical knowledge of plant operation and maintenance in addition to the common safety practices.
Here, we are not just focusing on answering "how" questions. We are more concerned with answering the "why" questions. This course offers a valuable opportunity to expand your understanding of P&IDs and their importance in real-world applications.
Starting from reading and understanding P&IDs, we shall dive deeper into the reasons behind different guidelines and practices, providing valuable insights into their significance.
Course Overview
This course gives a clear understanding of essential topics related to Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs). Throughout this course, we delve into vital details that should be included in a P&ID, equipping you with the knowledge to interpret and analyze these crucial documents accurately.
We begin by exploring the common data shown for equipment, piping, instruments, control systems, shutdown systems, and pressure safety valves. In addition, we shall cover the anatomy and different types of P&IDs (e.g. legend, distribution and tie-in P&IDs), enabling you to comprehend various P&ID representations and apply them smoothly.
Operational and maintenance guidelines play a significant role in ensuring smooth process functioning. That's why we shall delve into isolation philosophies for equipment and maintenance requirements. You'll gain insights into the purpose of closed drain and open drain systems and understand the distinctions between them. Furthermore, we explore plant depressurization and blowdown requirements and their impact on the flare system.
The course emphasizes critical process safety requirements. We'll see the importance of specifying proper design pressures and temperatures for equipment and piping to ensure inherent plant safety. We'll also cover fail-safe positions for valves based on anticipated hazards and upset scenarios.
In situations where an inherently safe system cannot be achieved, we shall examine layers of protection for the plant, including operator intervention, prevention, and mitigation of hazards. Each layer is carefully considered when preparing P&IDs to enhance overall safety.
To assess the adequacy of protection measures, we explore Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) and Safety Integrity Level (SIL) assessments, supported by practical examples that deepen your understanding of these fundamental risk assessment techniques.
Join us on this comprehensive P&ID course and gain a profound understanding of these topics, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to effectively analyze, interpret, and implement P&IDs in diverse industries.
Who this course is for:
- Chemical Engineering Student Looking for Learning Practical Engineering Concepts
- Process Engineers looking for enhancing their P&ID Preparation Skills
- Plant Operation Engineers willing to understand the behind-the-scene concepts of plant design and share solutions to enhance the safety and operability of your plant.
- Non-Process Engineers for example, a piping or instrumentation or mechanical engineer who wants to understand the criticality of process engineering requirements and how your role affects the plant performance
What is this Course About?
Explore the details and structure of P&IDs, and gain practical knowledge of plant operation and maintenance in addition to the common safety practices.
Here, we are not just focusing on answering "how" questions. We are more concerned with answering the "why" questions. This course offers a valuable opportunity to expand your understanding of P&IDs and their importance in real-world applications.
Starting from reading and understanding P&IDs, we shall dive deeper into the reasons behind different guidelines and practices, providing valuable insights into their significance.
Course Overview
This course gives a clear understanding of essential topics related to Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs). Throughout this course, we delve into vital details that should be included in a P&ID, equipping you with the knowledge to interpret and analyze these crucial documents accurately.
We begin by exploring the common data shown for equipment, piping, instruments, control systems, shutdown systems, and pressure safety valves. In addition, we shall cover the anatomy and different types of P&IDs (e.g. legend, distribution and tie-in P&IDs), enabling you to comprehend various P&ID representations and apply them smoothly.
Operational and maintenance guidelines play a significant role in ensuring smooth process functioning. That's why we shall delve into isolation philosophies for equipment and maintenance requirements. You'll gain insights into the purpose of closed drain and open drain systems and understand the distinctions between them. Furthermore, we explore plant depressurization and blowdown requirements and their impact on the flare system.
The course emphasizes critical process safety requirements. We'll see the importance of specifying proper design pressures and temperatures for equipment and piping to ensure inherent plant safety. We'll also cover fail-safe positions for valves based on anticipated hazards and upset scenarios.
In situations where an inherently safe system cannot be achieved, we shall examine layers of protection for the plant, including operator intervention, prevention, and mitigation of hazards. Each layer is carefully considered when preparing P&IDs to enhance overall safety.
To assess the adequacy of protection measures, we explore Hazard and Operability (HAZOP) and Safety Integrity Level (SIL) assessments, supported by practical examples that deepen your understanding of these fundamental risk assessment techniques.
Join us on this comprehensive P&ID course and gain a profound understanding of these topics, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to effectively analyze, interpret, and implement P&IDs in diverse industries.
Who this course is for:
- Chemical Engineering Student Looking for Learning Practical Engineering Concepts
- Process Engineers looking for enhancing their P&ID Preparation Skills
- Plant Operation Engineers willing to understand the behind-the-scene concepts of plant design and share solutions to enhance the safety and operability of your plant.
- Non-Process Engineers for example, a piping or instrumentation or mechanical engineer who wants to understand the criticality of process engineering requirements and how your role affects the plant performance
User Reviews
Rating
Boostrand Training
Instructor's CoursesBoostrand PE
Instructor's Courses
Udemy
View courses Udemy- language english
- Training sessions 101
- duration 5:02:28
- Release Date 2023/08/01