Computer Networks & Data Communication Essentials
Dr. Moazzam Tiwana
6:44:34
Description
A Comprehensive Guide to Internet Technologies: From Basics to Advanced Protocols and Security Measures
What You'll Learn?
- Computer Network Essentials
- StackHow Internet & Computer Networks Work?
- Over All TCP/IP Protocol Stack
- Important Application Layer Protocols
- TCP & UDP as Transport Layer Protocls
- IP Addressing: Classless InterDomain Routing (CIDR)
- Working of Switches & Routers
- Different Routing protocols & their comparison
- NAT, ICMP, ARP
- Multiple Access Protocols: ALOHA, Slotted ALOHA, CSMA/CD
- Ethernet Protocol
- Virtual LANS (VLANs)
Who is this for?
What You Need to Know?
More details
DescriptionThis meticulously designed program is tailored for beginners and aspiring IT professionals, providing a solid foundation in the core principles of computer networking & data communication. Whether you're a student venturing into the world of technology or a professional looking to strengthen your skills, this course offers a practical and accessible approach to understanding the fundamentals of computer networks.
By the end of this course, you will have a comprehensive understanding of computer network essentials, empowering you to navigate the dynamic world of networking confidently. Join us on this educational journey, and let's build a strong foundation for your success in the exciting field of computer networks!
Sections Breakdown:
Introduction to Computer Networks:
Explore the essentials of the internet, dissecting the components that form its backbone.
Understand the roles of hosts, clients, and servers in network communication.
Navigate through the Access Network, Core Network, and the overall architecture of the internet.
Gain insights into the layers of the Internet Protocol (IP) stack.
Application Layer:
Dive into networking applications and their design principles, including Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer architectures.
Learn the intricacies of processes communicating through sockets.
Explore protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS that drive internet applications.
Understand the working of web caches and the BitTorrent file-sharing application.
Transport Layer:
Differentiate between the Transport and Network layers.
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP, delving into their segment structures and flow control mechanisms.
Explore the intricacies of the TCP three-way handshake and connection closure.
Network Layer:
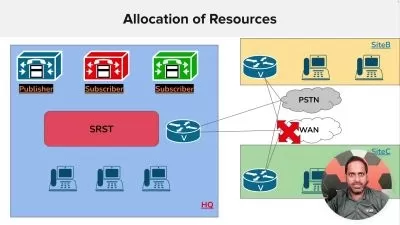
Understand the functions of routers, focusing on routing and forwarding.
Grasp the nuances of IP addressing, subnets, and hierarchical addressing.
Explore dynamic protocols like DHCP and NAT, essential for efficient network management.
Gain insights into routing types, including static and dynamic, and Inter-AS routing protocols like BGP.
Learn about ICMP, IPv6, and the complexities of routing on the Internet.
The Link Layer:
Delve into the services provided by the Link Layer, covering framing, link access, reliability, and more.
Understand the role of network interface cards (NIC) and the communication between adjacent nodes.
Explore multiple access protocols, controlled access protocols, and address resolution with ARP.
Learn about Ethernet, switches, and the motivation behind using Virtual LANs (VLANs).
The Physical Layer:
Trace the evolution of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standards and common implementations of fast Ethernet.
Computer Network Security:
Gain insights into firewalls, their types, and their critical role in network security.
Explore stateless and stateful packet filtering, application gateways, and best practices for securing computer networks.
Join us on this educational journey, where you'll not only learn the essentials but also delve into advanced protocols and security measures.
Who this course is for:
- Beginners in IT and networking field
This meticulously designed program is tailored for beginners and aspiring IT professionals, providing a solid foundation in the core principles of computer networking & data communication. Whether you're a student venturing into the world of technology or a professional looking to strengthen your skills, this course offers a practical and accessible approach to understanding the fundamentals of computer networks.
By the end of this course, you will have a comprehensive understanding of computer network essentials, empowering you to navigate the dynamic world of networking confidently. Join us on this educational journey, and let's build a strong foundation for your success in the exciting field of computer networks!
Sections Breakdown:
Introduction to Computer Networks:
Explore the essentials of the internet, dissecting the components that form its backbone.
Understand the roles of hosts, clients, and servers in network communication.
Navigate through the Access Network, Core Network, and the overall architecture of the internet.
Gain insights into the layers of the Internet Protocol (IP) stack.
Application Layer:
Dive into networking applications and their design principles, including Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer architectures.
Learn the intricacies of processes communicating through sockets.
Explore protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DNS that drive internet applications.
Understand the working of web caches and the BitTorrent file-sharing application.
Transport Layer:
Differentiate between the Transport and Network layers.
Compare and contrast TCP and UDP, delving into their segment structures and flow control mechanisms.
Explore the intricacies of the TCP three-way handshake and connection closure.
Network Layer:
Understand the functions of routers, focusing on routing and forwarding.
Grasp the nuances of IP addressing, subnets, and hierarchical addressing.
Explore dynamic protocols like DHCP and NAT, essential for efficient network management.
Gain insights into routing types, including static and dynamic, and Inter-AS routing protocols like BGP.
Learn about ICMP, IPv6, and the complexities of routing on the Internet.
The Link Layer:
Delve into the services provided by the Link Layer, covering framing, link access, reliability, and more.
Understand the role of network interface cards (NIC) and the communication between adjacent nodes.
Explore multiple access protocols, controlled access protocols, and address resolution with ARP.
Learn about Ethernet, switches, and the motivation behind using Virtual LANs (VLANs).
The Physical Layer:
Trace the evolution of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standards and common implementations of fast Ethernet.
Computer Network Security:
Gain insights into firewalls, their types, and their critical role in network security.
Explore stateless and stateful packet filtering, application gateways, and best practices for securing computer networks.
Join us on this educational journey, where you'll not only learn the essentials but also delve into advanced protocols and security measures.
Who this course is for:
- Beginners in IT and networking field
User Reviews
Rating
Dr. Moazzam Tiwana
Instructor's Courses
Udemy
View courses Udemy- language english
- Training sessions 158
- duration 6:44:34
- Release Date 2024/01/04