CFD analysis of ONERA M6 wing - Part 3 CFD and validation
Sijal Ahmed
2:18:17
Description
CFD analysis of ONERA M6 wing using Fluent and validation with AGARD experimental data and high quality CFD from NASA
What You'll Learn?
- To conduct CFD analysis of ONERA M6 wing in particular and CFD analysis of any wing or aerodynamic body in general
- How to get high quality data from literature for validation
- Understanding drag, lift and pitching moment coefficient and reference values
- Setting up problem in Fluent and accelerating convergence
- Effect of turbulence model and Y+ values on aerodynamic coefficient
- Validating present CFD with avaiable experimental data and high quality CFD from NASA
- Effect of different solvers on results
Who is this for?
More details
DescriptionIn this course you will learn about CFD analysis of ONERAÂ M6 wing. First we will go through problem descriptions and given operating conditions. After that we will discuss about the different aerodynamic coefficients such as lift coefficient and reference conditions. I will also explain that how to calculate reference area, pressure, density etc. from Reynolds number and Mach number. We will then discuss about the experimental data for Cp plots. We will then go through different literature to explore the CD, CL and CM as these are not given in experimental work by AGARD published in 1979. But fortunately NASAÂ has published high quality CFD data for Cp and CL, CD and CM for different solvers and mesh types. Therefore we will use NASA data to compare drag, lift and pitching moment coefficients.
After this all discussion we will import mesh into Fluent. Mesh is already created in ICEMCFD hexa in part 2. We will set boundary conditions, operating conditions, material properties, solver type, reference values, report definitions and finally we will initialize solution and run the simulation.
Once solution is fully converged, we will extract Cp and aerodynamic coefficients. We will compare them with available data. Finally I will explain method to get Cp plot and import it into excel. Then I will teach you how to non dimensionalize axis and Cp data and plot it in excel. Experimental data for Cp will be plotted in same graph. We will use NASA Cp plot and plot it in same plot to compare our CFD, experimental data from AGARD and CFD data from Fluent.
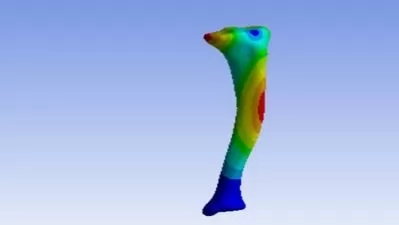
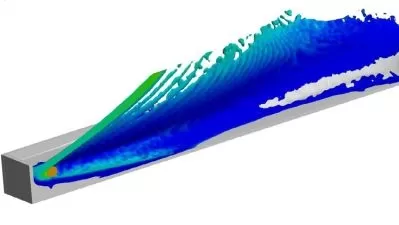
ONERA M6 is a classical test case for CFD validation. Although geometry is simple, but the flow field involves complex flow features such as transonic flow (Mach No. 0.7 - 0.92) with shocks, boundary layer separation etc. The ONERA M6 wing was designed in 1972 by the ONERA Aerodynamics Department as an experimental geometry for studying three-dimensional, high Reynolds number flows. ONERA is a swept back wing, with half span. It is external third of M5 Wing without twist.
In this three part course series, you will learn about the conducting CFD analysis of ONERA M6 wing as per data given by AGARD AR 138 1979 by Schmitt, V. and F. Charpin.
Learning outcomes of this course:
1. At the end of this three part course/tutorial, student will be able to perform CFDÂ simulation of exteneral, viscous, compressible flow around 3D geometry at transonic conditions using various turbulence models and appropriate Y+ values.
2. Student will be able to understand/learn all processes involved in high fidelity CFD analysis such as geometry creation, meshing, CFD setup, solution and post processing.
3. Student will be able to validate CFD results against experimental data from AGARD report.
4. Following things will be covered:
Geometry generation in Solidworks
Hemisphere domain in Spaceclaim
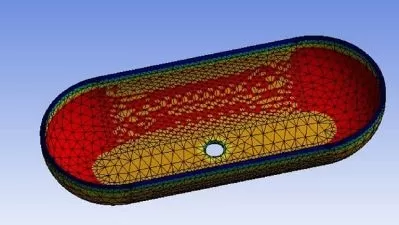
Hexa meshing in ICEMCFD
Mesh import, boundary conditions specification, material properties, solver settings, report definitions, hybrid initialization etc.
Steady state, 3D Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes
Spalart-Allmaras, K-Epislon, Shear Stress Transport SST and transition turbulence models
2nd order upwind flow scheme
Compressible, implicit solver
No slips wall, Symmetry and pressure Far-Field boundary conditions
Convergence acceleration using latest options in Fluent 2022 R1
Parallel solver
Post processing of results
Validations of results against experimental data.
solution convergence assessment based on lift and drag coefficients.
Resources:
You will get following resources in this courseÂ
1. All power point slides
2. AGARD Report
3. All files including geometry, domain, hexa mesh, solved case and data files, excel file for data, aerofoil coordinates and also geometry from NASA.
Problem Setup
This problem will solve the flow past the wing with these conditions:
Freestream Temperature = 288.15 K
Freestream Mach number = 0.8395
Angle of attack (AOA) = 3.06 deg
Reynolds number = 11.72E6
Mean aerodynamics chord = 0.64607 m
Who this course is for:
- Students pursuing career in mechanical or aerospace engineering
- Processionals who want to enhance their CFD skills to advanced level
- Any CFD enthusiast who want to expand his skill level
In this course you will learn about CFD analysis of ONERAÂ M6 wing. First we will go through problem descriptions and given operating conditions. After that we will discuss about the different aerodynamic coefficients such as lift coefficient and reference conditions. I will also explain that how to calculate reference area, pressure, density etc. from Reynolds number and Mach number. We will then discuss about the experimental data for Cp plots. We will then go through different literature to explore the CD, CL and CM as these are not given in experimental work by AGARD published in 1979. But fortunately NASAÂ has published high quality CFD data for Cp and CL, CD and CM for different solvers and mesh types. Therefore we will use NASA data to compare drag, lift and pitching moment coefficients.
After this all discussion we will import mesh into Fluent. Mesh is already created in ICEMCFD hexa in part 2. We will set boundary conditions, operating conditions, material properties, solver type, reference values, report definitions and finally we will initialize solution and run the simulation.
Once solution is fully converged, we will extract Cp and aerodynamic coefficients. We will compare them with available data. Finally I will explain method to get Cp plot and import it into excel. Then I will teach you how to non dimensionalize axis and Cp data and plot it in excel. Experimental data for Cp will be plotted in same graph. We will use NASA Cp plot and plot it in same plot to compare our CFD, experimental data from AGARD and CFD data from Fluent.
ONERA M6 is a classical test case for CFD validation. Although geometry is simple, but the flow field involves complex flow features such as transonic flow (Mach No. 0.7 - 0.92) with shocks, boundary layer separation etc. The ONERA M6 wing was designed in 1972 by the ONERA Aerodynamics Department as an experimental geometry for studying three-dimensional, high Reynolds number flows. ONERA is a swept back wing, with half span. It is external third of M5 Wing without twist.
In this three part course series, you will learn about the conducting CFD analysis of ONERA M6 wing as per data given by AGARD AR 138 1979 by Schmitt, V. and F. Charpin.
Learning outcomes of this course:
1. At the end of this three part course/tutorial, student will be able to perform CFDÂ simulation of exteneral, viscous, compressible flow around 3D geometry at transonic conditions using various turbulence models and appropriate Y+ values.
2. Student will be able to understand/learn all processes involved in high fidelity CFD analysis such as geometry creation, meshing, CFD setup, solution and post processing.
3. Student will be able to validate CFD results against experimental data from AGARD report.
4. Following things will be covered:
Geometry generation in Solidworks
Hemisphere domain in Spaceclaim
Hexa meshing in ICEMCFD
Mesh import, boundary conditions specification, material properties, solver settings, report definitions, hybrid initialization etc.
Steady state, 3D Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes
Spalart-Allmaras, K-Epislon, Shear Stress Transport SST and transition turbulence models
2nd order upwind flow scheme
Compressible, implicit solver
No slips wall, Symmetry and pressure Far-Field boundary conditions
Convergence acceleration using latest options in Fluent 2022 R1
Parallel solver
Post processing of results
Validations of results against experimental data.
solution convergence assessment based on lift and drag coefficients.
Resources:
You will get following resources in this courseÂ
1. All power point slides
2. AGARD Report
3. All files including geometry, domain, hexa mesh, solved case and data files, excel file for data, aerofoil coordinates and also geometry from NASA.
Problem Setup
This problem will solve the flow past the wing with these conditions:
Freestream Temperature = 288.15 K
Freestream Mach number = 0.8395
Angle of attack (AOA) = 3.06 deg
Reynolds number = 11.72E6
Mean aerodynamics chord = 0.64607 m
Who this course is for:
- Students pursuing career in mechanical or aerospace engineering
- Processionals who want to enhance their CFD skills to advanced level
- Any CFD enthusiast who want to expand his skill level
User Reviews
Rating
Sijal Ahmed
Instructor's Courses
Udemy
View courses Udemy- language english
- Training sessions 7
- duration 2:18:17
- Release Date 2022/12/31