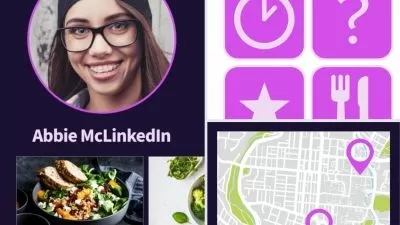
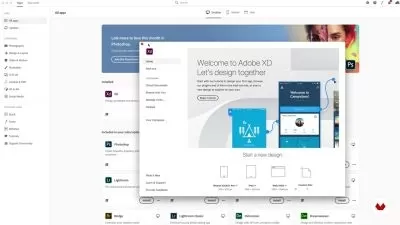
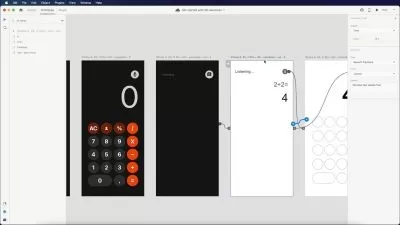
About Adobe XDLearn More
Adobe XD is a software platform created for user experience (UX) designers to create prototypes of user interfaces and mobile web applications. With built in collaboration tools, XD enables designers to share mockups across teams for feedback and input. The design tools that XD provides allows creators to reuse elements, such as buttons and navigation components, from one design to the next, allowing consistency of design and user experience.
Sort by:
Sorting
The newest
Most visited
Course time
Subtitle
Filtering
Courses

Udemy


James Joab Soren
UI/UX Design Masterclass with Adobe XD: From Beginner to Pro 3:51:03
05/19/2024
Subtitle
UdemyAdobe Xd Create Prototypes Mobile Application And Web Design
7:32:59
English subtitles
05/08/2024
Subtitle

SkillShare


Aleksandar Cucukovic
Adobe Xd Masterclass - UI / UX Design From Scratch 20:14:08
English subtitles
02/17/2024
Subtitle
SkillShareUXUI Design Design Beautiful Messaging App with Adobe XD
1:58:41
English subtitles
02/12/2024
Frequently asked questions about Adobe XD
Adobe XD is an experience design platform used to create realistic prototypes and mockups for website and app development. Adobe XD allows for streamlined and efficient collaboration; the platform can support Adobe Creative programs like Photoshop, Illustrator, along with Slack and Microsoft Teams. Shareable libraries keep all assets organized and accessible. With Adobe XD, graphic designers and production teams can turn ideas into workable previews to test navigation, user experience, and device responsiveness. Eventual website developers and other key stakeholders can be invited into the process early on to transition from prototype to live site as smoothly as possible.
Designers across many different industries use Adobe XD to develop creative mockups. Website designers can incorporate cohesive branding and navigational components with Repeat Grid and the stacks and padding features. App designers can use Adobe XD’s Responsive Resize feature and pre-built artboards to build experiences for different devices and screen sizes efficiently. Graphic designers who work in marketing and advertising may use the platform to lay out a new campaign; Adobe XD allows design teams to integrate consistent branding and messaging over a variety of social apps and websites. Adobe XD is also used in voice assistance design and game design.
Alternatives to Adobe XD include Sketch, a vector-based platform with a focus on user interfaces for website and app design. Figma is another vector-based option that emphasizes collaboration between designers and other teams; Figma is primarily accessible online but does include offline capabilities. Balsamiq Wireframes is a simple wireframing and user interface tool that mimics the experience of drawing by hand. Wondershare Mockitt, UXPin, Abstract, Draftium, Moqups, and InVision Studio are a few other Adobe XD alternatives for prototype development.
Adobe XD and Adobe Photoshop serve two different design purposes but can be used in conjunction with one another. Adobe Photoshop is a raster-based program designed to create, edit, and manipulate photos and other artwork. While Photoshop can build a web page or app mockups, that’s not the platform’s main purpose. Adobe XD is designed first and foremost to help designers build true-to-life prototypes of websites, apps, marketing campaigns, and more. Adobe XD also incorporates team collaboration and workflow management into the process through integration with Slack and Microsoft Teams. Elements designed in Photoshop will likely be utilized in Adobe XD as a project progresses.
Adobe XD is a vector-based platform. Vector graphics are based on mathematical formulas and render as points, lines, and curves. This means that vector artwork is scalable; no matter how big or small a vector graphic is sized, the image will not lose quality. As Adobe XD is intended for user experience design across a wide variety of screen sizes, social media apps, and industries, a vector-based platform makes sense. Designers and collaborators can feel confident that they’re seeing and testing accurate representations of their final product. Raster-based artwork is rendered in pixels, and these images will lose quality as they are resized.